Zeppelins and Airships
|
NASM exhibit - reserve
|
1783 - On June 4, Joseph and Jacques Montgolfier demonstrated the first hot air balloon in Annonay, France, that rose to 6,562 feet. On Oct. 15, Jean François Pilatre de Rozier and Marquis d'Arlandes made the first manned flight in a Montgolfier hot-air balloon.
1852 - Henri Giffard in France added a steam engine to his balloon and created the first airship, or dirigible, defined as a lighter-than-air ship with propulsion and steering capability.
1864 - Ferdinand Zeppelin visited America and made aerial observations in a Union Army balloon during the Civil War.
1891 - Otto Lilienthal began successful gliding experiments.
1896 - Samuel P. Langley produced successful steam-powered models that could fly, during the Airship Craze of the '90s.
1898 - On Sept. 18, Brazilian Alberto Santos-Dumont in Paris flew the first gasoline-powered airship.
1900 - Count Ferdinand Graf von Zeppelin in Germany constructed the first rigid-frame airship, the LZ 1 (Luftschiff Zeppelin 1), and flew it on July 2 with 5 passengers. The aluminum frame was covered with cloth and held 17 hydrogen cells, was 420 ft. long, 38.5 ft diamter, shaped like a cigar, 2 Daimler engines in 2 gondolas, each only 15 hp, and flew up to 1300 ft.
1901 - Alberto Santos-Dumont, Brazilian aviator, circled Eiffel Tower in his gasoline-powered airship.
1904 - Thomas Baldwin flew his 53-foot airship, the California Arrow, at the St. Louis World's Fair.
1908 - Thomas Baldwin made the first airship for the U. S. Army Signal Corps, the SC-1, powered by a Curtiss aircraft engine.
1909 - Count Zeppelin in November founded world's first commercial airline, DELAG, or the German Airship Transportation Company.
1910 - Count Zeppelin launched the improved airship Deutschland that became the LZ 10.
1911 July 15 - LZ 10 became the first commercial passenger airship, the "Schwaben," piloted by Dr. Hugo Eckener, carried 1553 passengers in 218 flights until burned in 1912. More airships were added to the line, each carried 20 passengers in cabin with wicker furniture, cold menu, wine list.
1911 Oct. 17 - rival Schutte-Lanz firm, flew SL 1, had been founded 1909 in Mannheim.
1912 - The first war airship was the L 1 launched Oct. 7.
1914 - Germany had 10 zeppelins at the start of the First World War in August. German engineer Hugo Eckener took over the Zeppelin company on the death of its founder in 1917, and led the construction of 67 zeppelins by 1918.
1915 - On Jan. 19, German zeppelins began bombing raids over the British coast. On May 31, the LZ-38 became the first zeppelin to bomb London, but in 1916 England and France pulled fighter planes from the Western Front to attack zeppelins with phosphorous ammunition.
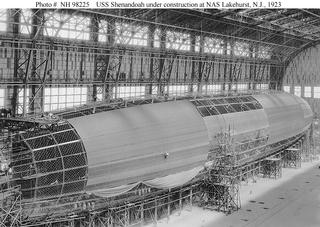
1917 - On Oct. 2, the L-49 was captured in France intact, and American engineers used this zeppelin as the model for the ZR-1, or USS Shenandoah, built 6 years later. On Oct. 19, eleven high-altitude zeppelins attacked England from 20,000 ft., beyond the range of fighter planes.
1918 - On Aug. 8, Germany launched its last zeppelin raid over England, but a De Haviland DH-4 shot down the L-70 at 17,500 ft., the lead ship of three long-range zeppelins that were to continue on to bomb New York. The other two ships, the L-53 and L-65 returned to Germany.
1919 - The Versailles Treaty forbade Germany to possess airships, but Hugo Eckener arranged to build airships under contract with the U. S. Navy.
|
USS Shenandoah, from NHC
|
1924 - Eckener delivered the ZR-3 airship to the U. S. Navy, renamed the USS Los Angeles, that would make 331 flights by 1932. The restrictions of the Versailles Treaty were rescinded and Eckener's Zeppelin Company was allowed to build German airships, including the Graf Zeppelin and the Hindenburg.
1925 - On Sept. 3, the USS Shenandoah crashed in Ohio during a thunderstorm, killing its crew of 14.
1929 - In August, with financing by William Randolph Hearst, the Graf Zeppelin circled the globe in 12 days after flying from Friedrichshaften, Germany, to start the epic voyage from Lakehurst, NJ.
1933 - On Apr. 4, the USS Akron crashed off the Atlantic coast, killing 73 of its crew, including Admirial William Moffett. On Oct. 16, the Akron's sister ship, the USS Macon, made its maiden voyage from Ohio to Moffett Field in Californa.
1935 - On Feb. 12, the USS Macon crashed into the ocean off Monterey, Californa. The government put a halt on rigid airship construction.
1936 - In May, the Hindenburg began regular service to America.
1937 - On May 6, the Hindenburg was destroyed in a fire at Lakehurst, NJ.
1942 - In Jan., the U. S. Navy commissioned its first blimp squadron, ZP-32, stationed at Moffett Field.
Links:
- Timeline of Flight from Library of Congress
- Hindenburg feature film from 1975
- Lighter-Than-Air Society and the Akron Airship Historical Center.
- Moffett Field
- Navy Lakehurst Historical Society includes the USS Shenandoah (ZR-1) and USS Los Angeles (ZR-3) and USS Akron (ZRS-4) and Hindenburg (LZ-129)
- The Height Climbers about the WWI airships designed to bomb London and New York from 20,000 ft.
- The Zeppelin from Centennial of Flight
- Zeppelin NT manufactured by ZLT Zeppelin Luftschifftechnik GmbH & Co
- Zeppelin raids on the Hartlepools in 1916
- (on reserve) Hindenburg home movies of 1937 and J. Gordon Vaeth article "What Happened to the Hindenburg?"
Sources:
- Archbold, Rick and Ken Marschall. Hindenburg An Illustrated History. NY: Warner Books, 1994.
- Botting, Douglas. Dr. Eckener's Dream Machine : the Great Zeppelin and the Dawn of Air Travel. New York : Henry Holt, 2001.
- De Syon, Guillaume. Zeppelin! : Germany and the Airship, 1900-1939. Baltimore : Johns Hopkins University Press, 2002.
- De Syon, Guillaume. "The Zeppelin Museum in Friedrichshafen," Techonology and Culture, Jan. 1999, pp. 114-119.
- Dick, Harold G. and Douglas H. Robinson. The Golden Age of the Great Passenger Airships, Graf Zeppelin & Hindenburg. Washington, D.C. : Smithsonian Institution Press, 1985.
- Meyer, Henry C. Airshipmen, Businessmen, and Politics, 1890-1940. Washington : Smithsonian Institution Press, 1991.
- Robinson, Douglas H. The Zeppelin in Combat : a History of the German Naval Airship Division, 1912-1918. Seattle : University of Washington Press, 1994. 4th ed.